RFID, NFC
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. The tags contain electronically stored information. Passive tags collect energy from a nearby RFID reader's interrogating radio waves and therefore do not need a power source like a battery.
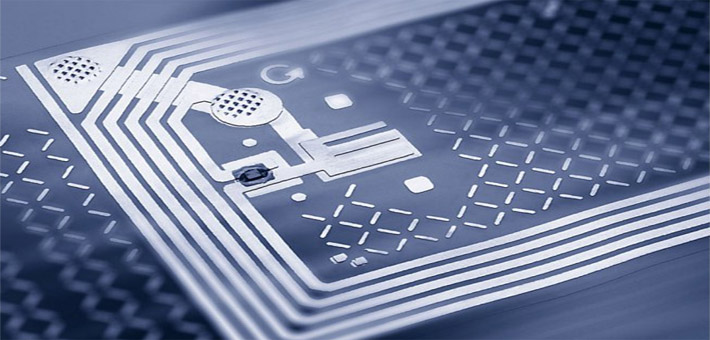
The RFID tag can be affixed to an object and used to track and manage inventory, assets, people, etc. For example, it can be affixed to cars, computer equipment, books, mobile phones, etc. RFID offers advantages over manual systems or use of bar codes. The tag can be read if passed near a reader, even if it is covered by the object or not visible. The tag can be read inside a case, carton, box or other container, and unlike barcodes, RFID tags can be read hundreds at a time. Bar codes can only be read one at a time using current devices.
What isthe difference between RFID and NFC?
RFID is the process by which items are uniquely identified using radio waves, and NFC is a specialized subset within the family of RFID technology. Specifically, NFC is a branch of High-Frequency (HF) RFID, and both operate at the 13.56 MHz frequency. NFC is designed to be a secure form of data exchange, and an NFC device is capable of being both an NFC reader and an NFC tag. This unique feature allows NFC devices to communicate peer-to-peer.

Applications
- Contactless payments
- Access management
- Tracking of goods
- Tracking of persons and animals
- Machine readable travel documents
- Baggage tracking logistics
- Tracking and billing processes
